Thyroid Gland – Must Known Facts
Do you have hair loss or weight gain? Or is it just the opposite? Do you feel any change in your energy level or mood? If yes, put the blame on your Thyroid Gland. Regardless of its small size, this gland acts as a great regulator of the body and mind. It is considered to be the ‘powerhouse’ of the human body. Let us dig into more facts about this wonderful gland.
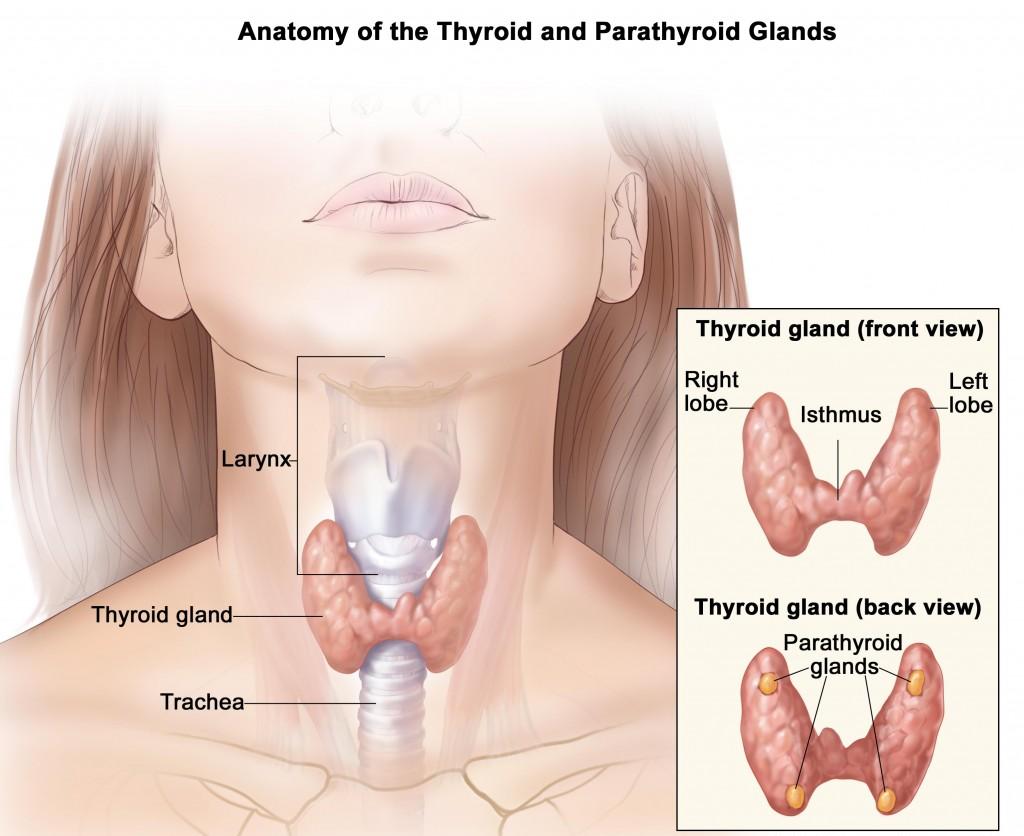
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland situated in the front lower part of our neck. It produces two hormones namely Tetraiodothyronine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) and they travel through the bloodstream and affect almost every part of your body, from tip to toe. T4 and T3 hormones regulate your metabolism which affects your body temperature, heart rate and the way you burn your calories etc.
There are mainly two types of thyroid conditions that could happen due to the inappropriate production of thyroid hormones.
1) Hyperthyroidism
In this condition, the thyroid becomes overactive by producing too much of T4, T3 or both. Hyperthyroidism can make your bones weak and thin which leads to osteoporosis.
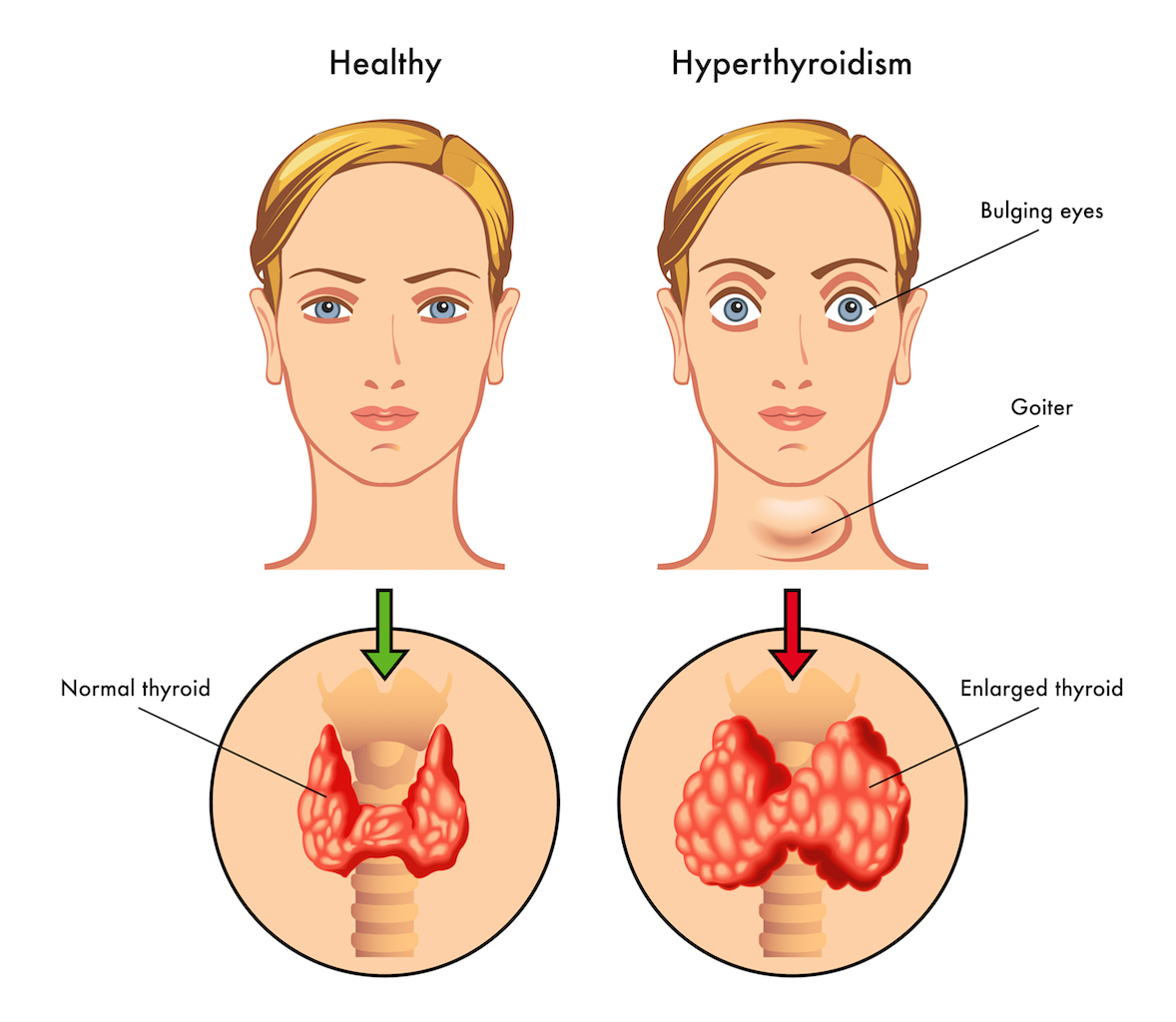
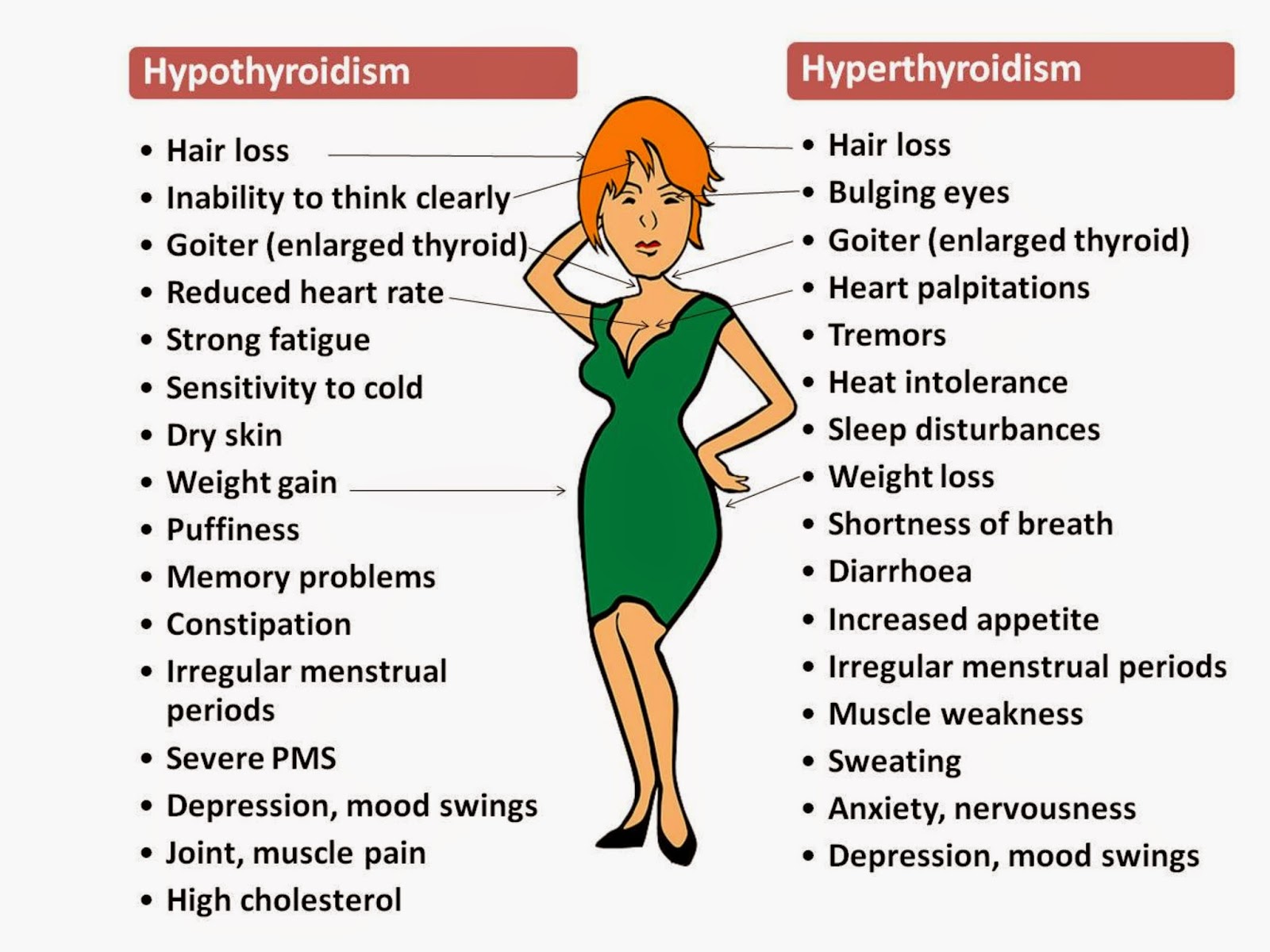
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
-
High metabolic rate resulting from high amount of T4, T3 or both. This would lead to further complications like weight loss, rapid heart rate, elevated blood pressure, hand tremors, sweating, diarrhoea and in women, irregular menstrual cycles.
-
Thyroid nodules
-
Goitre – swelling of the thyroid, which can be either symmetrical or one-sided and eyes may appear protruded.
-
Inability to concentrate, nervousness, difficulty to sleep, fine or brittle hair, hair loss, breast development in men, nausea and vomiting.
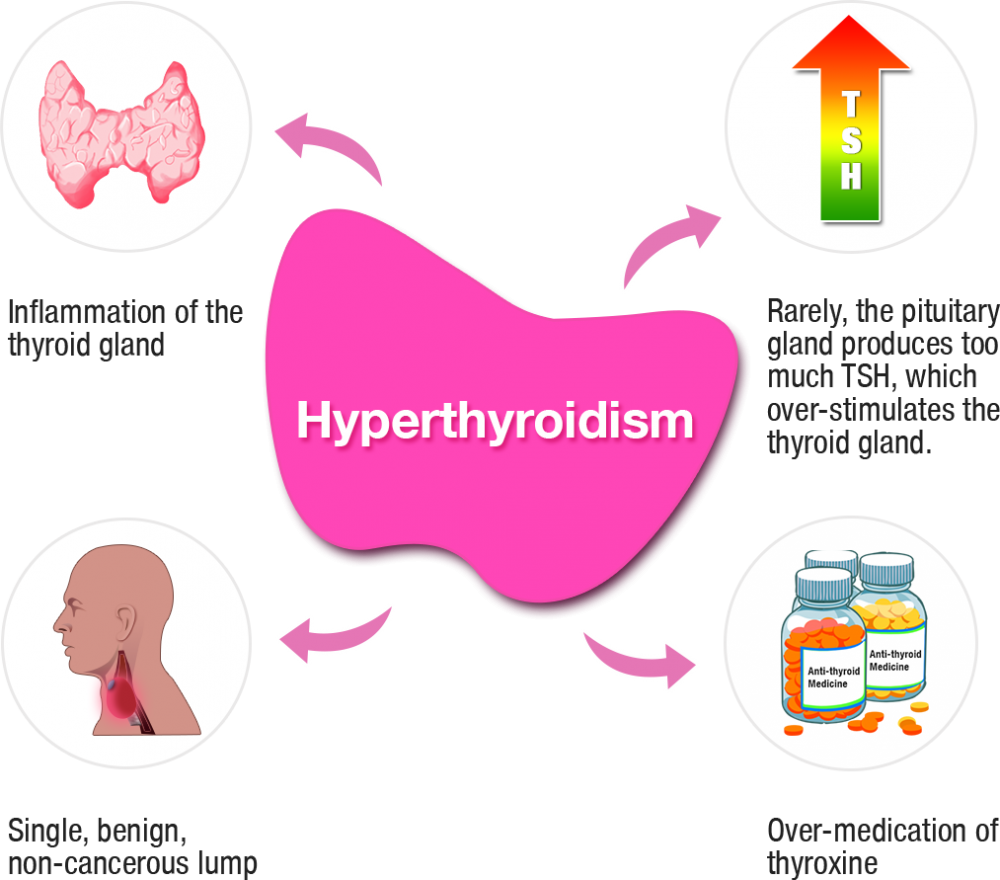
Causes of hyperthyroidism
-
Grave’s disease: It is an autoimmune disorder with hereditary nature, affecting the thyroid, particularly, the skin and eyes. The prime visible symptom is that there will be an uncomfortable swelling behind the eyes. It is also accompanied by an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid, termed goitre and an increase in thyroid hormone production. Fatigues, weight loss, abnormal intolerance of heat, muscle weakness, protruded eyeballs are some common symptoms of Grave’s disease. This occurs more often in women than in men.
-
An excess amount of iodine which is a key ingredient in T4 and T3.
-
Inflammation of the thyroid termed thyroiditis that causes hormones to leak out of gland tumors of ovaries or testes.
-
A large amount of T4 consumed through dietary supplements or medications.
Diagnosis of hyperthyroidism
You need to get a complete medical history and physical exam with various tests.
-
Cholesterol test – Low cholesterol level can be a sign of hyper metabolic state.
-
T4, free T4, and T3 – This test gives the measurement of thyroid hormones (T4 and T3) in your blood.
-
TSH level test – Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is secreted by the pituitary gland and this hormone stimulates the thyroid to produce T4 and T3. An abnormally low-level TSH is a unique sign of hyperthyroidism.
-
Triglyceride test – Low triglyceride level indicates a hyper metabolic state.
-
Ultrasound – This scan measures the size of your thyroid and any tumors.
-
CT or MRI – Doing any one of these scans will help you reveal if there are any tumors present in your pituitary.
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
-
Anti-thyroid medications.
-
Radioactive iodine helps to destroy the cells that produce T4 and T3 very effectively.
-
Surgery – A part or the whole of your thyroid may be removed through surgery. After that, you would have to take thyroid hormone supplements to prevent hypothyroidism.
2) Hypothyroidism
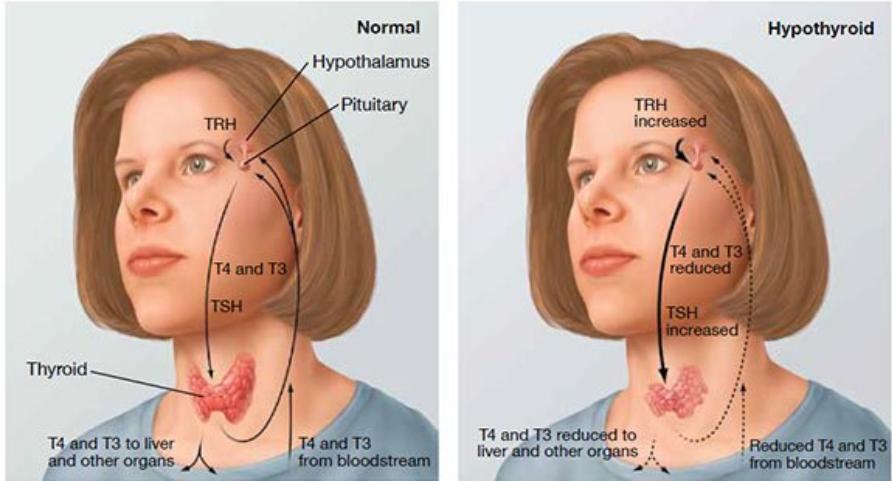
Here the underactive thyroid gland is not producing enough amounts of T4 and T3. The result is that your activities will slow down; your metabolic rate becomes sluggish. Older women are more prone to hypothyroidism. Race (white or Asian), age (growing older), autoimmune disorders like Type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, bipolar disorder, Down syndrome are some of the risk factors associated with this condition.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
-
Weight gain – as your metabolic rate would be low.
-
Swelling of the thyroid – goiter.
-
Your heart rate will be slower than usual.
-
Less active and depressed.
-
Dry hair and hair loss.
-
Greater sensitivity to cold, as thyroid disorders will hinder the body’s ability to regulate temperature.
-
Constipation
-
Dry and brittle nails
-
Irregular menstrual cycle
-
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) caused by swelling of the median nerve near to the wrist bone.
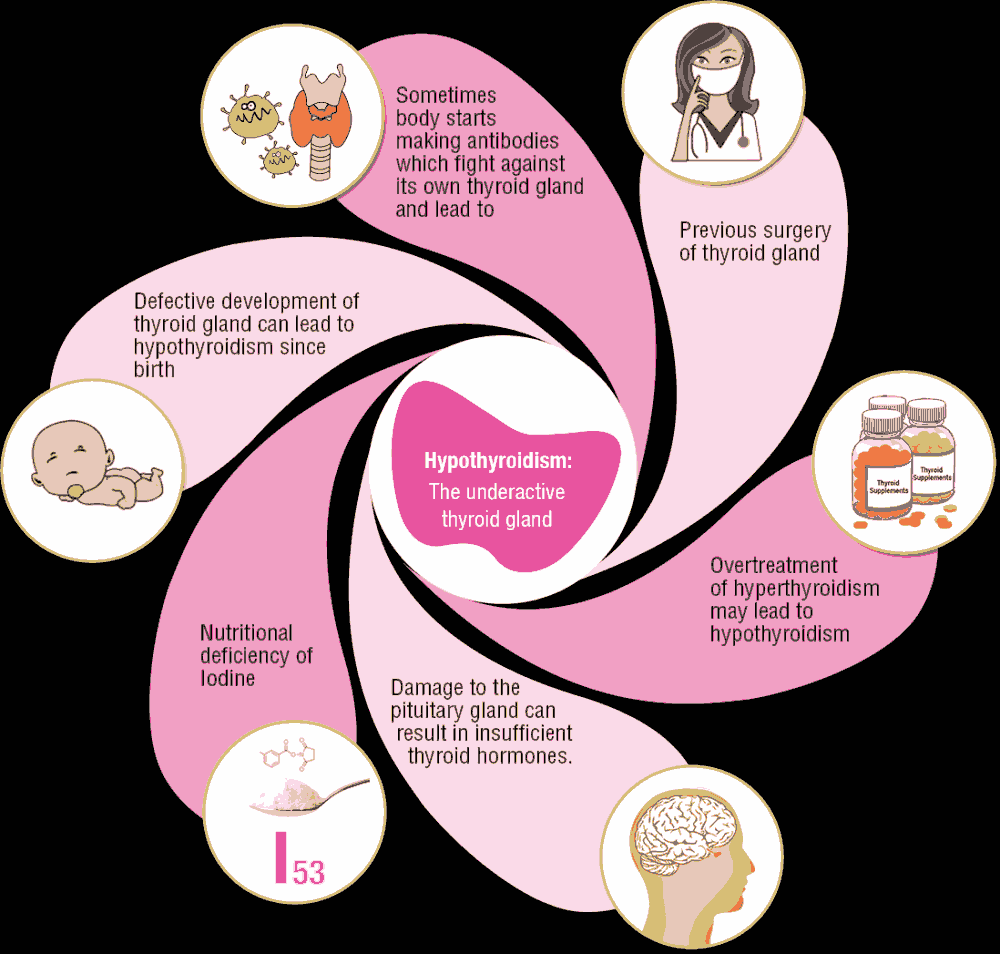
Causes of hypothyroidism
-
Hashimoto’s Disease: It is an autoimmune disorder of hereditary nature where your body produces antibodies that could attack and destroy your thyroid. It may also be caused by viral infection.
-
Radiation therapy in the neck region: Radiation therapy for cancer, especially in the neck region might cause damage to your thyroid cells making it difficult to produce hormones.
-
Radioactive iodine treatment: This destroy the cells in the thyroid making it less functional.
-
Medication: Use of certain medicines may hinder your thyroid’s ability to produce hormones.
-
Iodine in the diet: Thyroid needs iodine for hormone production and lack of it would lead to hypothyroidism.
-
Pregnancy: Postpartum thyroiditis where there is a severe increase in thyroid hormone production followed by a sharp drop in the same.
-
Congenital Hypothyroidism: It is a condition in which some babies may be born with a thyroid that is not well developed or not functioning properly.
-
Pituitary & Hypothalamus Gland: Any damage or disorder to your pituitary and hypothalamus would lead to hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism
Many of its symptoms are similar to other diseases and so, it has to be diagnosed with the help of the following tests.
-
TSH test: Generally, normal TSH level is a sign of hypothyroidism. A slight elevation in the TSH level without symptoms is termed Mild or Subclinical Hypothyroidism. This condition is often seen as an early stage in hypothyroidism.
-
T4 test: In hypothyroidism, the T4 level may be lower than normal.
-
If your thyroid test results are abnormal, your doctor may prescribe a thyroid ultrasound or a scan to check the presence of thyroid nodules or inflammations.
Treatment of hypothyroidism
-
Daily dose of Synthetic Thyroxine pills.
-
The patient’s age, weight, the severity of hypothyroidism etc. need to be monitored.
-
TSH levels are monitored 6 to 8 weeks after the pill is administered and the dose is adjusted accordingly.
Prevention is the Key
Follow a healthy diet. There is no particular food plan which is good for thyroid conditions, but make sure that you don’t overeat. You need to include lots of fruits that are good in antioxidants such as grapes, apple, berries etc. Limit consumption of red meat as it contain saturated fats. Try to include seafood in your diet as these are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and iodine. Cashew nuts, almonds, pumpkin seeds are good sources of iron and selenium that support the thyroid. Having green leafy vegetables which are rich in magnesium, helps to fight fatigue, muscle cramps etc.
Following a balanced and healthy diet, doing proper workouts and regular checkups would help you a lot to overcome these thyroid conditions, its symptoms and other risk factors. So, do not ignore the symptoms, go for regular check-ups and take care of your ‘power house’ thyroid gland. It’s never too late….BE HEALTHY AND STAY HEALTHY!!!




Recent Comments